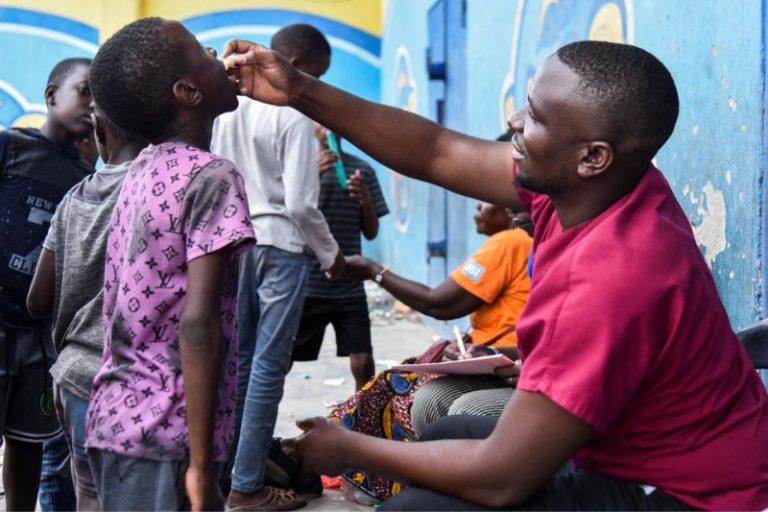
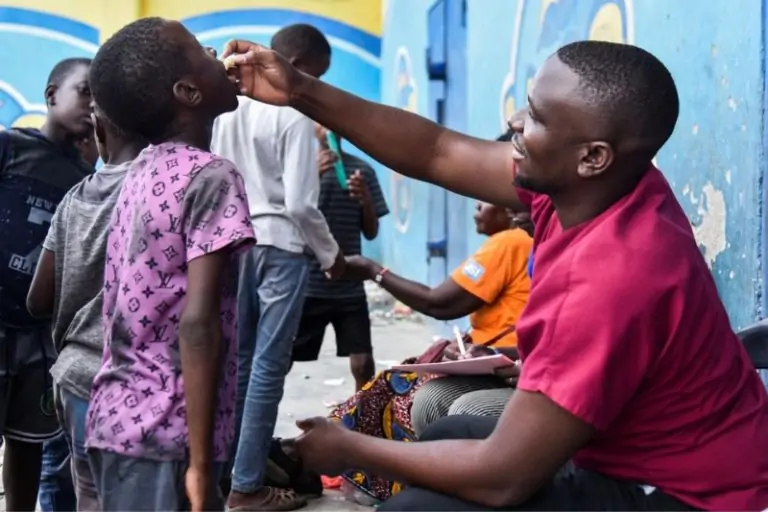
cholera outbreak in zambia schools closed stadiums converted to hospitals
In the wake of a massive cholera outbreak claiming over 400 lives and infecting more than 10,000 people, Zambian authorities have extended school closures after the year-end holidays. The epidemic has prompted unique measures, such as converting a major soccer stadium in the capital into a substance abuse treatment center.
The Zambian government has declared a state of emergency, activating the National Disaster Management Agency. In a bid to curb the spread of cholera, a mass immunization program has been initiated, and clean water delivery, totaling 2.4 million liters per day, is underway across the nation.
Cholera, a bacterial infection causing severe diarrhea, is often linked to contaminated food or water. Its prevalence is closely tied to inadequate access to clean water and poverty. The outbreak, which began in October, has reached alarming proportions, affecting nearly half of Zambia’s districts and nine out of ten provinces.
As of the latest report by the Zambia Public Health Institute, there have been 10,413 reported cases and 412 fatalities. The country, with a population exceeding 20 million, faces a grave health security threat, with over 400 daily cholera cases recorded. According to UNICEF, the fatality rate is “devastatingly high” at 4%.
Cholera outbreaks have plagued southern Africa, affecting countries like Malawi, Mozambique, and Zimbabwe. In 2023 alone, the region reported over 200,000 illnesses and 3,000 deaths. Malawi experienced its most severe cholera outbreak in decades. Globally, around thirty nations, including Nigeria and Uganda, have grappled with severe cholera epidemics in recent years.
Dr. Mazyanga Mazaba, head of public health strategy and communication, notes that Zambia has witnessed significant cholera outbreaks since the 1970s. However, the current epidemic ranks as the most severe in terms of reported cases in the past two decades. Climate factors, such as heavy rains and storms, contribute to the persistence of cholera.
In response to the outbreak, the Zambian government announced the postponement of school openings until January 29, emphasizing alternative educational programs through public television and radio. The Disaster Management and Mitigation Unit activated water supply initiatives, including enormous tanks and daily water deliveries, along with the distribution of granulated chlorine for water treatment.
Zambia has received 1.4 million doses of the oral cholera vaccine from the World Health Organization (WHO), with an anticipation of over 200,000 additional doses. The government, including Health Minister Sylvia Masebo, publicly received vaccinations to encourage widespread immunization. Global health experts warn of a strain on vaccine supplies, with shortages expected until 2025.
The cholera outbreak in Zambia underscores the urgent need for comprehensive public health measures, vaccination campaigns, and global collaboration to address waterborne diseases and mitigate their impact on vulnerable populations.
Beyond the immediate health crisis, the cholera outbreak in Zambia is causing severe socioeconomic repercussions. The disruption of economic activities is notable, especially in regions grappling with instability. Sudan, for instance, is anticipating a twelve percent drop in economic activity due to ongoing violence, impacting global commodity markets and neighboring countries.
Addressing displacement challenges in Africa requires a collaborative effort, and the private sector plays a crucial role. The Amahoro coalition’s co-founder, Isaac Kwaku Fokuo, emphasizes the economic impact of displacement, stressing that private sector involvement provides sustainable solutions. Investments in conflict zones not only stimulate economic activity but also contribute to future workforces and infrastructure development.
The Africa Cup of Nations (AFCON) 2024 is poised to serve as a significant economic driver for the Ivory Coast. Industries such as entertainment, hospitality, and fashion are strategically capitalizing on the event’s potential, despite facing economic challenges. Entrepreneurs are leveraging the heightened demand for experiences beyond the competition, presenting a positive economic outlook amid existing concerns.
Angola’s decision to withdraw from the Organization of the Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC) due to disagreements over oil output limitations raises geopolitical questions. This unexpected move prompts inquiries about its impact on Angola’s position in the international oil scene and its broader implications within OPEC and OPEC+. The energy sector is closely monitoring this development and its potential ramifications.
Tensions between Ethiopia and Somalia take center stage at an extraordinary session of the Intergovernmental Authority on Development (IGAD). The summit addresses the contentious memorandum of agreement (MoU) between Somaliland and Ethiopia, sparking opposition from the Somali government, which deems it a violation of sovereignty. IGAD‘s facilitative role and the withdrawal of Sudan from the summit add complexity to the ongoing diplomatic challenges.
The escalating refugee crisis in Africa, marked by a rise from 36 million to 45 million forcibly relocated individuals between 2021 and 2023, necessitates sustainable solutions. Private sector interventions in regions hosting refugees prove pivotal. Isaac Kwaku Fokuo emphasizes the dual benefits of private sector involvement, citing it as an investment in economic activity and future workforces while fulfilling a moral imperative for collective growth.
Angola’s departure from OPEC and the evolving energy landscape in Africa raise critical questions about the continent’s energy future. Balancing oil output, geopolitical dynamics, and regional cooperation are pivotal in shaping Africa’s energy trajectory. The private sector’s role in driving sustainable energy solutions becomes increasingly significant amid these challenges.
The cholera outbreak in Zambia remains a grave health and security threat, prompting extensive measures to curb its spread. The conversion of a soccer stadium into a treatment center and the activation of the National Disaster Management Agency underscore the severity of the situation. Mass immunization, clean water distribution, and global vaccine supply concerns highlight the multifaceted efforts required to address waterborne diseases in vulnerable populations.
The U.S.-based driver training company Zutobi analyzed road safety worldwide and found South Africa stays last in driving danger since…
The Basketball Africa League (BAL) returns for its 2025 season with exciting changes and developments. Since 2019 the NBA-linked basketball…
The Somali president supports their military forces to eliminate the threats from Al-Shabaab, ISIS, and Al-Qaeda. The Somali National Army…
UAE President Sheikh Mohamed bin Zayed Al Nahyan held talks with President Faustin Archange Touadéra of the Central African Republic…
African football teams struggle intensely in the World Cup Qualification rounds to earn their place on the international football stage.…
The journey toward the 2026 FIFA World Cup is rapidly intensifying for all African teams, who now hold a historical…
This website uses cookies.