Last updated on September 11th, 2021 at 02:52 pm
The 1918 influenza pandemic – called the “Spanish flu” – remains the most significant public health event ever recorded in human history.
It’s estimated that half a billion people were infected, and that between 20 million and 100 million people died. Most deaths occurred in Asia (36 million). In Africa 2.5 million died, Europe 2.3 million and North America 1.6 million.
The exact origin of the flu is still unclear. Some reports indicate that it first occurred and spread within the US in 1918.
A more recent study suggests the pandemic originated in China in 1917, and was introduced into Canada and the US by Chinese labourers. Soldiers, returning home after the end of World War I, then brought it to Europe and the rest of the world.
The Spanish flu is believed to have come to Kenya with returning veterans who docked in the Mombasa port. The country was still a British colony at the time. In nine months the epidemic killed about 150,000 people, between 4% and 6% of the population at the time.
In a recent study, my colleagues and I examined the impact of the Spanish flu in coastal Kenya. We chose the coastal province because it was the colony’s most critical administrative area, due to its port in Mombasa.
It also had better administrative and health records. Vital data from this period is incomplete and biased, so we examined narratives of how the pandemic affected people’s lives.
We saw that there were various forms of social and economic disruption, ranging from social distancing to the suspension of nonessential services, paralysed administrative operations, widespread food shortages, commercial losses, and an overwhelmed healthcare sector.
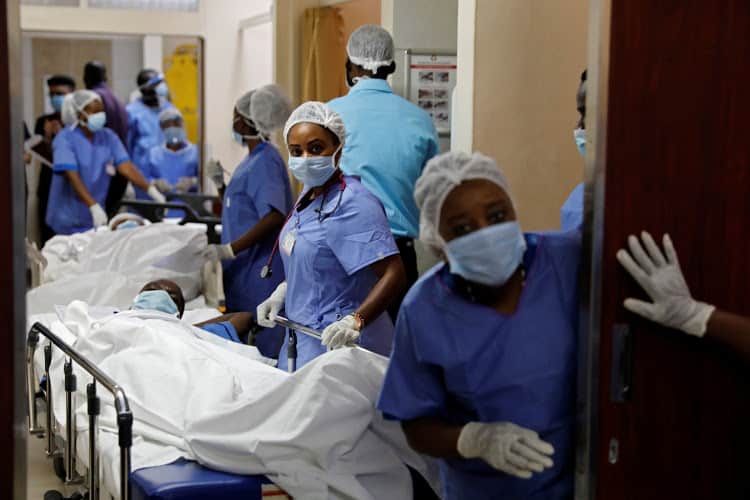
Kenya is battling a new pandemic: Covid-19. Even though it’s 100 years later, the new coronavirus has echoes of those experiences a century ago.
The flu spread rapidly For our study we used colonial records and correspondence from Kenya’s National Archives Library in Nairobi.
The interactions between district and provincial level administrations on the pandemic were key sources.
They included the minutes of local chiefs’ weekly meetings, health facility case and death summaries, case report forms, district officers’ letters and routine district briefs.
In the same period (1912-1925), the entire Coast Province (seven districts) had a population that ranged between 170,000 and 243,841 people.
We focused on five of the seven districts with data on pandemic cases: Kilifi (previously Nyika), Kwale (previously Vanga), Mombasa, Taita Taveta and Malindi.
Before the Spanish flu came, patient visits to healthcare facilities varied between 9 and 33 for every 1,000 people per year.By 1918 this had increased five-fold, to 146.8 visits.
Similarly, trends of mortality increased sharply from 1918, from less than five deaths per 1,000 people per year to 25 deaths. This high mortality rate continued through to 1925.
We found that the Spanish flu spread rapidly, and had a high mortality rate. In just nine months – from September 1918 to June 1919 – there were approximately 31,908 cases and 4,593 deaths associated with the Spanish flu in Kenya’s coastal province. In the same period, 150,000 deaths were reported across the country.
A century ago, the Spanish flu caused untold suffering and social disruption to hundreds of thousands of locals. We can argue that the mitigation efforts and medical advances of the time did little.In addition, what brought it into the country – global war and colonial rule – were beyond the control of locals.
But what stands out is that the actions of locals, individually and collectively, contributed to the sickness and death. We found that most locals disregarded quarantine measures and, in the peak of the outbreak, went to their rural villages. This amplified community transmission.
In the Covid-19 pandemic, we can draw parallels and learn from our past.
(TheStar)
Two mobile telecom leaders, MTN Group and Airtel Africa, joined forces to create a new digital infrastructure system throughout African…
South African President Cyril Ramaphosa defended his nation against claims of white discrimination made by tech magnate Elon Musk. After…
Hilton launched Signia by Hilton for its first appearance in Egypt and Africa through its hotel expansions. These hotels at…
UNICEF reported that, nearly 2900 people died of cholera across Eastern and Southern African countries while children suffer most greatly…
Enza, based in the United Arab Emirates, obtained $6.75 million in initial investment funding from Algebra Ventures and Quona Capital.…
US Secretary of State Marco Rubio ordered South African Ambassador Ebrahim Rasool to leave America by March 21 because he…
This website uses cookies.