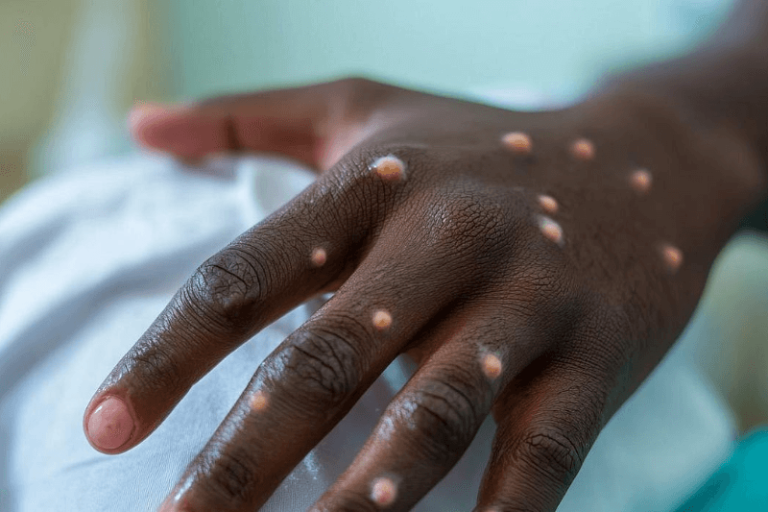

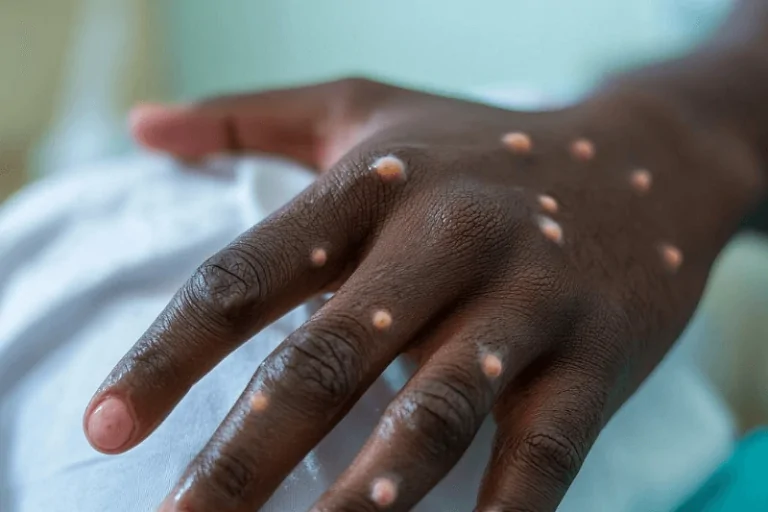
mpox virus resurgence in the drc calls attention to global health issues
Once known as monkeypox, the Mpox virus is resurging throughout several areas and the epicenter of this concerning epidemic is the Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC). Particularly given that more than 70% of the cases have been recorded among minors, the DRC’s position is grim with over 18,000 cases documented and at least 500 deaths.
The DRC’s continuous insurgency makes managing the outbreak difficult, but the World Health Organisation (WHO) is working nonstop to guarantee a strong response. The incident manager for Mpox at the WHO Regional Office for Africa, Dr. Samuel Boland, underlined the ways the agency reaches even the most conflict-torn areas.
“We can reach folks who might otherwise be difficult to reach by foot using tools like the radio. Dr. Boland added, “We have already started the process of organizing a sizable workforce across the DRC and other Mpox-affected areas who are already on the ground and ready to support the Mpox response in these very tough and hard-to-reach areas.”
The Congolese health minister says the DRC should get vaccination doses in response to the issue next week. The WHO has underlined the immediate need of these vaccinations.
“DRC’s initial doses of the vaccination will arrive just the next few weeks. The most important thing to keep in mind is that vaccinations in the hands of the critical groups that require them—that is, those who want them—are what we need not vaccinations on the tarmac. Dr. Boland further said, “We are already working very hard with member states and partners to develop national vaccination plans so that as soon as those vaccines arrive on the ground, we can distribute them to the people who need them as quickly as possible.”
As the epidemic progressed throughout several African nations last week, the WHO declared Mpox a global health emergency. The company underlines that the most efficient approach to stop the virus from spreading could be preventive systems.
“Building knowledge and awareness helps one to guarantee prevention. People must be aware of the indicators and know how to stop one person from passing on their symptoms to another. Stopping transmission just requires people to maintain public health and social measures, such avoiding physical contact with others if they are unwell; vaccination is not always necessary.” Dr. Boland stated.
Reiterating worldwide unity and preemptive actions to stop additional spread, the WHO has informed the people that this epidemic is not another COVID-19.
The U.S.-based driver training company Zutobi analyzed road safety worldwide and found South Africa stays last in driving danger since…
The Basketball Africa League (BAL) returns for its 2025 season with exciting changes and developments. Since 2019 the NBA-linked basketball…
The Somali president supports their military forces to eliminate the threats from Al-Shabaab, ISIS, and Al-Qaeda. The Somali National Army…
UAE President Sheikh Mohamed bin Zayed Al Nahyan held talks with President Faustin Archange Touadéra of the Central African Republic…
African football teams struggle intensely in the World Cup Qualification rounds to earn their place on the international football stage.…
The journey toward the 2026 FIFA World Cup is rapidly intensifying for all African teams, who now hold a historical…
This website uses cookies.